At Saimona Compressed Air with decades of experience, we combine technology, reliability and expert service to keep your operations running smoothly. We deliver high-performance, durable and energy-efficient air compressors to industries across India. From industrial air compressors to screw air compressors, our solutions are designed to meet the evolving needs of manufacturing units, workshops, construction sites and HVAC providers. Saimona Compressed Air is founded with a vision to provide world-class compressed air solutions which has become a trusted name among industrial operations across India. Over the years, we have expanded our expertise to deliver customized, energy-efficient and reliable compressors to clients ranging from small workshops to large manufacturing plants.
We pride ourselves on combining technical expertise, high-quality engineering, and hands-on support to ensure our clients receive products that last longer and perform better. Our team works closely with industries to understand their unique requirements, offering solutions that optimize efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain operational continuity.
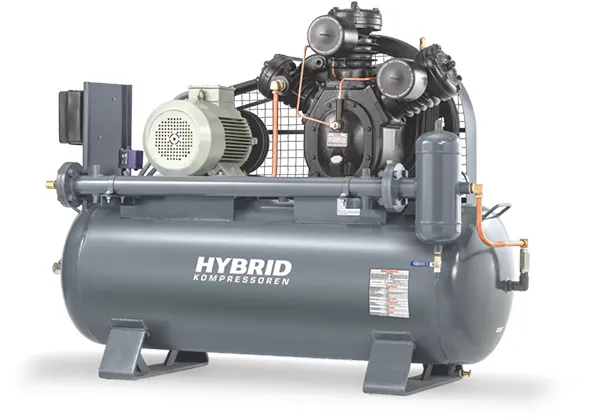
Our screw air compressor is engineered for energy efficiency, low maintenance and smooth operation, making it ideal for large-scale factories and production lines requiring continuous compressed air supply.
.webp)
High-performance compressors designed for continuous operation in manufacturing units and workshops. Built for durability and efficiency, they deliver consistent airflow under demanding industrial conditions.
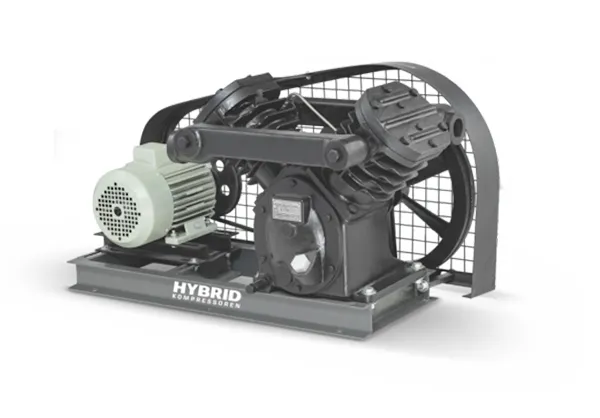

Compact, versatile, and easy to deploy, these compressors suit workshops, construction sites, and mobile operations—providing convenience without compromising performance or reliability.
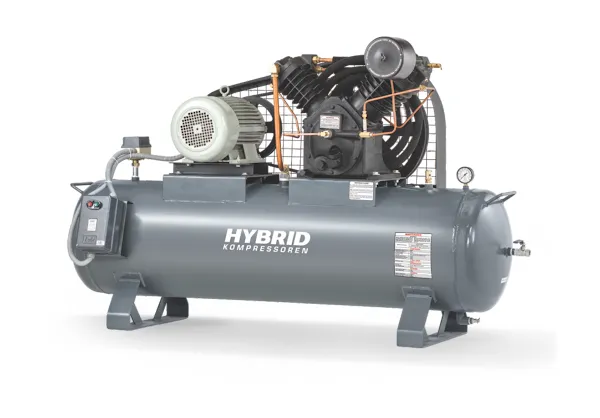

We provide complete compressed air solutions including piping, filters, dryers and essential accessories to enhance system efficiency and ensure longer operating life.
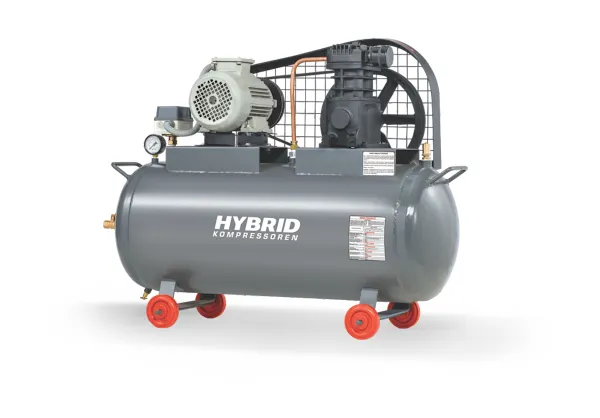

Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and extended service life. Our expert team provides onsite support, troubleshooting, and preventive maintenance tailored to your industrial requirements.
Yes. Our screw air compressors and industrial units are designed for low energy consumption while maintaining consistent performance.